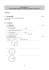File
Transcription
File
Practice Test Gr. 9 Chapter 2 and 3 Please return this copy when you have finished! Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Multicellular organisms use mitosis for a. growth b. sexual reproduction c. repairing damaged tissue d. both A and C ____ 2. Red blood cells have a lifespan of approximately four months. New red blood cells are always being produced by a. mitosis b. regeneration c. budding d. the cell cycle ____ 3. The activities of a cell are controlled by its a. nucleus b. nucleolus c. nuclear membrane d. ribosomes ____ 4. The number of chromosomes in a cell is a. the same for all living things b. related to how big the organism grows c. different for every living thing d. the same within members of the same species ____ 5. At any given time, most of the cells in your body are in a. interphase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase ____ 6. The brain cells presently working to answer this question are in a. interphase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase ____ 7. Chromosomes are replicated during a. interphase b. prophase c. anaphase d. Telophase ____ 8. The cells in a dog’s body contain 78 chromosomes. After mitosis has taken place, the resulting cells each have a. 39 chromosomes b. 78 chromosomes c. 156 chromosomes d. one-half of every chromosome ____ 9. The stages of mitosis, in the order that they take place, are a. anaphase, metaphase, prophase, telophase b. prophase, anaphase, metaphase, telophase c. prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase d. prophase, telophase, metaphase, anaphase ____ 10. Any substance that can cause a mutation in the genes controlling cell division is known as a. a hazardous industrial chemical b. an environmental pollutant c. a carcinogen d. a cytokinetic agent ____ 11. Bacteria can double their numbers rapidly under ideal conditions using a. binary fission b. budding c. vegetative reproduction d. spores ____ 12. You are observing an animal you have never seen before and you notice what looks like a baby growing out of its side. Investigation of the “baby” shows that it has the same genes as the larger animal. What you have observed would be described as a. sexual reproduction b. budding c. vegetative reproduction d. fragmentation ____ 13. Strawberry plants often send out runners that grow into new plants. What is true of these new plants? a. They are genetically identical to the original plant. b. They are natural clones of the original plant. c. They have been produced by vegetative reproduction. d. All of the above are true. ____ 14. If you look at the underside of a mushroom you will find tiny spores hidden inside the gills. These spores a. all have the same DNA b. are the seeds of the mushroom c. are the mushroom’s form of sexual reproduction d. are the zygotes of a mushroom ____ 15. If a crab loses a claw, it will often grow a new claw. The detached claw will not grow a whole new crab. This describes a. asexual reproduction b. fragmentation c. regeneration d. Budding ____ 16. Which of the following is not true of asexual reproduction? a. Only one parent is needed. b. The offspring are genetically identical to one another. c. Variations are introduced into the population. d. Large numbers of offspring can be produced. ____ 17. Why might meiosis be necessary for a species? a. to produce somatic cells with half the number of chromosomes, so that when they reproduce, the zygotes will have the same number as the parents b. to produce sex cells with half the number of chromosomes, so that when they combine, the zygotes will have the same number as the parents c. to produce sex cells with a complete set of chromosomes, so that when they combine, the gametes will have the same number as the parents d. to produce somatic cells with a random number of chromosomes, so that the offspring are genetically different from their parents ____ 18. What cells undergo mitosis in an organism? a. somatic sex cells b. cells which produce gametes c. all somatic cells d. gametes ____ 19. What cells undergo meiosis in an organism? a. somatic sex cells b. gametes c. all somatic cells d. cells which produce gametes ____ 20. The chromosomes in a diploid cell are in pairs. the two chromosomes which make up one pair are called a. similar chromosomes b. analogous chromosomes c. somatic chromosomes d. homologous chromosomes ____ 21. A human has 23 pairs of chromosomes. If the gene for tongue curling is found on one chromosome, then a. it may or may not be found on any other chromosome b. it will not occur on any other chromosomes c. it will also be found at the same point on the homologous chromosome d. it will also be found at the same point on all 23 chromosomes ____ 22. An ape has 24 pairs of chromosomes. How many chromosomes does an ape zygote have? a. 48 b. 24 c. 12 d. 23 Figure 3.1 ____ 23. In Figure 3.1, the correct sequence of events is a. 1,2,5,4,3 b. 2,3,4,5,1,4 c. 3,4,1,2,5 d. 2,3,1,4,5 ____ 24. In Figure 3.1, in which stage represents anaphase? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 ____ 25. In Figure 3.1, in which stages are the chromatids in pairs? a. 1 and 3 only b. 1 only c. all stages d. 2 and 5 only ____ 26. In Figure 3.1, in which stage(s) is interphase represented? a. 1 b. 1 and 4 c. 3 d. 2 and 5 ____ 27. In Figure 3.1, what type of cell division is represented? a. mitosis b. meiosis c. meiosis I d. meiosis II ____ 28. An ape has 24 pairs of chromosomes. How many chromosomes does an ape egg have? a. 48 b. 24 c. 12 d. 23 ____ 29. Dogs and wolves each have 78 chromosomes. How many chromosomes does a dog sperm have? a. 156 b. 39 c. 78 d. 38 ____ 30. If a girl’s mother has blue eyes, and her father has brown eyes, the colour of her eyes would be determined by a. a combination of chromosomes from her parents b. which chromosome from her parents was first to be reproduced c. which allele from her parents was dominant d. which allele her mother gave her ____ 31. Meiosis is sometimes called “reduction division” because a. during meiosis the number of chromosomes is reduced to half b. there are 4 daughter cells instead of two, so they are smaller than in mitosis c. all the cells often do not survive, so there are not as many of them d. the amount of genetic information that can be passed by meiosis is less than in mitosis ____ 32. If meiosis did not reduce the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells, what might one problem be? a. sperm would be too large to swim to the egg b. there would be too many offspring c. the number of chromosomes in a species would double every generation d. soon organisms would be too large to survive ____ 33. A species’ genome is a. the number of chromosomes it has b. the type of cell division it uses c. the total of all its genes d. all its characteristics ____ 34. Diversity refers to a. offspring in a species spreading away from the parents b. the number of different cell types a species has c. having two separate sexes instead of one d. the amount of variation among different species ____ 35. The difference between alleles and genes is a. alleles are different forms of a gene b. genes are variants of alleles c. nothing, the two words mean the same thing d. all chromosomes have genes, only some have alleles ____ 36. Conjugation is a. a form of sexual reproduction in some bacteria b. another word for fertilization in some species c. another word for conception in plasmids d. sexual reproduction of individuals of different species ____ 37. A hermaphrodite is an organism that a. can reproduce sexually without sexual contact with another b. has both male and female organs in the same individual c. results from of problems during cell division d. changes sex from male to female at least once during its life ____ 38. An advantage for a hermaphroditic species would be that a. less information needs to pass in the genes, because only one form of the organism needs to be coded for. b. all individuals in the species are able to produce many more sperm and eggs to spread, thereby increasing the chance of them getting together. c. in species where individuals rarely come into contact with each other, both individuals can mate with each other. d. in species having both sexes in each individual makes it possible to reproduce sexually since they cannot move to each other. ____ 39. A particular flower has both male and female reproductive organs. a. This results in cross pollination b. This flower probably cannot self-fertilize c. This causes all offspring to be identical d. This results in a form of asexual reproduction ____ 40. Which of the following are considered female flower parts? a. stigma, style, pistil b. petal, sepal, ovary c. stamen, ovary, pollen d. stamen, anther, filament Matching Match the phase of the cell cycle with the best description of what happens during that phase. a. interphase d. anaphase b. prophase e. telophase c. metaphase f. cytokinesis ____ 41. nuclear membrane breaks down, sister chromatids are visible ____ 42. nuclear membrane forms, chromosomes get longer and thinner ____ 43. cell membrane pinches cytoplasm to divide cell ____ 44. cell is active, DNA is replicated ____ 45. sister chromatids line up along the middle of the cell Practice Test Gr. 9 Chapter 2 and 3 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: LOC: 2. ANS: LOC: 3. ANS: LOC: 4. ANS: LOC: 5. ANS: LOC: 6. ANS: LOC: 7. ANS: LOC: 8. ANS: LOC: 9. ANS: LOC: 10. ANS: LOC: 11. ANS: LOC: 12. ANS: LOC: 13. ANS: LOC: 14. ANS: LOC: 15. ANS: LOC: 16. ANS: LOC: 17. ANS: LOC: 18. ANS: LOC: 19. ANS: LOC: 20. ANS: LOC: D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: K OBJ: 2.1 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI1 | Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 K OBJ: 2.1 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI1 K OBJ: 2.2 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI2 U/A OBJ: 2.2 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI2 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 U/A OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 U/A OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 HMP OBJ: 2.5 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI4 K OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 HMP OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 U/A OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 HMP OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 U/A OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI1 | Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 K OBJ: 2.6 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5 K OBJ: 3.1 Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: 3.1 Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: 3.1 Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: 3.1 Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 21. ANS: LOC: 22. ANS: LOC: 23. ANS: LOC: 24. ANS: LOC: 25. ANS: LOC: 26. ANS: LOC: 27. ANS: LOC: 28. ANS: LOC: 29. ANS: LOC: 30. ANS: LOC: 31. ANS: LOC: 32. ANS: LOC: 33. ANS: LOC: 34. ANS: LOC: 35. ANS: LOC: 36. ANS: LOC: 37. ANS: LOC: 38. ANS: LOC: 39. ANS: LOC: 40. ANS: LOC: A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: Unit A - PLB1 B PTS: Unit A - PLB3 C PTS: Unit A - PLB3 B PTS: Unit A - PLB3 A PTS: Unit A - PLB3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 K OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI1 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI5 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI5 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI5 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI5 U/A OBJ: Unit A - Ch. 03 KI5 3.1 REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.1 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 3.3 MATCHING 41. ANS: LOC: 42. ANS: LOC: 43. ANS: B PTS: 1 Unit A - PLB1 E PTS: 1 Unit A - PLB1 F PTS: 1 LOC: 44. ANS: LOC: 45. ANS: LOC: 46. ANS: LOC: Unit A - PLB1 A PTS: 1 Unit A - PLB1 C PTS: 1 Unit A - PLB1 D PTS: 1 Unit A - PLB1 47. ANS: C PTS: 1 LOC: Unit A - PLB1 TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: REF: TOP: Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 K OBJ: 2.4 Unit A - Ch. 02 KI3 REF: K OBJ: 2.6 TOP: Unit A - Ch. 02 KI5