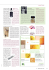la tête, le visage et le cou
Transcription
la tête, le visage et le cou
LA TÊTE,FACE LE VISAGE ET LE COU SKULL, AND NECK Évaluation de 1366of cas de comblement dermique fait avec l`implant Long-termtardive assessment 1366 cases of dermal d`acide hyaluronique dans le visage. filling with facial hyaluronic acid implants Introduction: Vanessa Contato Lopes Resende, Alessandra Haddad, Daniel Vasconcellos Regazzini,modifie Lydia Masako Le processus de vieillissement le contrôleFerreira facial et provoque la réduction de son volume avec des altérations dans la derme et Introduction: diminution du tissu sous-cutané.Des substances diverses ont été utilisées pour diminuer ces changements et compenser la forme The ageing process leads to alteration of the facial contours and reducvolumétrique tissulaire de la ride à travers le comblément dermique. tion of the overall volume due to deterioration of the dermis and loss of L`acide hyaluronique, à cause de ses caractéristiques biochimiques subcutaneous tissue. Several substances are being used to minimise , est l`agent choisi pour le traitement de comblément facial. Ses these deteriorations and to improve the volume and shape of wrinkle principales propriétés : biodégradable, appartient au groupe de tissue through dermal filling. Due its biochemical characteristics, hyaglycosamineglycanes qui font partie de la peau, hydrophile, inerte, luronic acid was the substance selected for this study of dermal filpeut être stérilisé, d action prolongée, d origine non-animal. ling. Its main properties are: it is biodegradable, it belongs to the group of glycosaminoglycans that form part of the skin, it is hydrophilic, inert Objectif: and sterlisable, it has a prolonged effect and is of non-animal origin. Fig. 1: schema de la zone d application de Figure one: diagram of the application l`acide hyaluronique en in sillon labial site of hyaluronic acid the naso nasolabial folds, upper and lower lip. et lèvreand supérieure et inférieure ( en(Filling jaune sites highlighted in yellow) les endroits du comblément. Fig. 2: two: coupe histologique avec ofdes Figure histological specimen fragments de peau avec implant d`acide a skin fragment with an intradermic implant of hyaluronic acid. hyaluronique intradermique. Fig. 3: three: photo de patiente soumise à une Figure Photograph of a patient application d`acide en hyasillon who underwent anhyaluronique application of luronic acid to the nasolabial folds. nasolabial. Figure four:de Photograph of the same Fig.4: photo la même patiente soumse who underwent application àpatient une application d`acide an hyaluronique em of hyaluronic acid to the nasolabial sillon nasolabial. folds. Évaluer l`efficacité et sécurité de l`acde hyaluronique comme comblément facial isolé, Objective: Méthode: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of hyaluronic acid for isolated dermal 1366 zones traitées ont été évaluées (injection entre 0,7 et 1,4 filling. ml d `acide hyaluronique, dans la derme réticulaire moyenne et aiguille 13x0,7 dans la derme réticulaire profonde et derme Method: papilaire), des produits de la marque Restylane et Perfectha® dans les evaluation zones suivantes: lèvres An was carriedsillon out ofnasolabial, 1366 sites of facial (fig.1), implantsdepressions of dermal fildueswithaux cicatrices et injection locales of avec peu 0.7 de and tissu sous-cutané ling hyaluronic acid (by between 1.4ml of sterilised en activité, systémique gestation, hyaluronic acid inpathologie a concentration of 20mg/ml,décompensée, using a 13 x 0.4 needle in the troubles de dermis cicatrisation, préventif avecreticular des substances mid-reticular and a 13traitement x 0.7 needle in the deep dermis and biodégradables. papillary dermis. The brands Restylane® and Perfecta® were used.) The sites were the following: nasolabial folds, lips (figure one), depressed scars Technique: and areas with a shortage of subcutaneous tissue. Exclusion criteria were Photo avant et aprèsacid, le traitement ( 30 et 180 jours).Signalisation allergies to hyaluronic active cutaneous pathologies, decompensated des zones qui doivent être traitées, le patient assis, procédure systemic pathologies, pregnancy, scarring disturbances and previous treatd`antispsie et application substances. d`anesthésique local photographs (lidocaïne 2%). ment with non-biodegradable Technique: were Injection du and produit la dose située 0,7days). et 1,4Marcation ml est faite taken before afterdont the treatment (at 30 entre and 180 was par rétropiqûres, faisant très attention pour pas hyperblock corriger, carried out with theenpatient seated. Antisepsis andne anaesthetic with suivieanaesthetic de compresses glacées pendant 10 minutes. local (lidocaine 2%) were used where indicated. The application by retro-injection of between 0.7 and 1.4ml was carried out, taking care not Résultats: to hypercorrect, followed by the use of a cold compress for 10 minutes. L`effet du comblément a été positif chez tous les patients avec un Results: haut degré de satisfaction. The effect of filling was appropriate in all patients, with satisfaction on Distribution, selon. la zone traitée : sillon naso labial (n= 658, 48,2%, discharge. The distribution according to the site of application was: nalèvres (n= 341, 25%), sillon nasolabial et lèvres (n= 260, 19%). solabial folds (n=658, 48.2%), lips (n=341, 25%), nasolabial folds and lobule de l`oreille (n= 16, 1,2%), région malaire (n=10, 0,7%) et lips (n=260, 19%), ear lobes (n=16, 1.2%), malar region (n=10, 0.7%) autres zones (n= 84, 6,1%). Il a fallu faire une retouche chez 32% and other sites (n=84, 6.1%). Retouching was needed in 32% of pades patients reévalués 15 jours plus tard. D`effets indésirables sont tients reassessed after 15 days. Adverse effects occurred in 164 pasurvenus chez 164 patients ( 12%) :ecchymose, asymétrie, nodules tients (12%), including ecchymosis, asymmetry, palpable nodules, palpables, oedème prolongé > 5 jours, récidive d`herpès labial prolonged oedema >5 days, recurrence of labial herpes and haemaet hématome. Des complications sont arrivées pour 8 patients toma. Complications occurred in eight patients (0.6%) including palpable (0,6%) : cordon fibreux palpable (2) ectropion (2) cellulite frontale(1) fibrous cord (2), ectropion (2), frontal cellulitis (1), foreign body granuloma granulome de corps étranger (1) et extrusion (2). Une patiente a (1) and extrusion (2). One patient developed nodules in the site of the fildéveloppé des nodules à l`endroit du comblément,on en a fait une ling. A biopsy was taken and it was concluded to be a sterile abscess. biopsie, résultant en abcès stéril. Discussion: Discussion: Une durée clinique variant de 8 mois à 1 an.. Les effets indésirables Clinical durability is between monthsnon and adéquate one year. The effects en général sont liés à laeight technique de adverse l`application are an inadequate application technique. Due the éviter risk of dugenerally produit.linked Pourtoéviter le risque de complications, on to doit complications, shouldles be avoided on the lower eyelids and the l`utilisation this du treatment produit dans paupières inférieur et glabelle. glabella. It was noted that when the filling ceased to be effective for the paOn a observé queinchez les patients dont l`effet du comblément tient and a repeat à application was et carried out, lowerbesoin quantities werenouvelle required commençaient s`estomper qui avaient d`une because of effects that hyaluronic acid has on the dermis (maintaining application, le volume nécessaire pour le même patient étaitspaces plus inpetit the fibrous hydration due to its pour dermal avoir lestructures même and effetimproving apportécutaneous par l`acide hyaluronique hydrophilic properties). (il soutient les fibres structurelles dermiques espacées et amélore l`hydratation cutanée parce qu`il est hydrophile). Conclusion: Conclusion: Hyaluronic acid is safe and effective for use as a dermal filler with a low risk of L`acide hyaluronique est fiable et agit comme produit destiné à complications and a high level of satisfaction. combler la derme, avec un faible risque de complications et un haut niveau de satisfaction. Références Bibliografiques: References: 1. Mausakiatti, W; Maibach, H I. Hyaluronic Acid and skin: wound healing and aging. Int J Dermatol, 1996, 35(8): 539-544. 1. Maibach H I, Hyaluronic and skin: wound healing andfor aging, 2. Mauskiatti Duranti, F;W;Salti, G; Bovani, B et al.Acid Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Gel SoftInternaTissue tional Journal of Dermatology, 1996, 35 (8): Augmentation. Dermatol Surg, 1998, 24:539-544 1317’1325. 2. Duranti F; Salti G; Bovani B et al., Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Gel for Soft Tissue Augmentation, Dermatologic Surgery, 1998, 24: 1317 -1325 Local de la réalisation de l`étude : UNIFESP – EPM, Dept.Cosmiatria e Laser – Sao Paulo - SP Study was carried out at UNIFESP EPM (Federal University of São Paulo), Cosmetic and Laser São Paulo, Brazil. Plastique , 2008 RévueUnit, Brésilienne de Chirurgie Volume 23 Numéro 3-2008 Supplément