Fonctions circulaires et hyperboliques
Transcription
Fonctions circulaires et hyperboliques
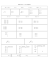
Fonctions circulaires et hyperboliques Propriétés trigonométriques : remplacer cos par ch et sin par i. sh. cos(a + b) = cos a. cos b − sin a. sin b cos(a − b) = cos a. cos b + sin a. sin b sin(a + b) = sin a. cos b + sin b. cos a sin(a − b) = sin a. cos b − sin b. cos a tan a + tan b tan(a + b) = 1 − tan a. tan b tan a − tan b tan(a − b) = 1 + tan a. tan b ch(a + b) = ch a. ch b + sh a. sh b ch(a − b) = ch a. ch b − sh a. sh b sh(a + b) = sh a. ch b + sh b. ch a sh(a − b) = sh a. ch b − sh b. ch a th a + th b th(a + b) = 1 + th a. th b th a − th b th(a − b) = 1 − th a. th b cos 2a = 2. cos2 a − 1 = 1 − 2. sin2 a = cos2 a − sin2 a sin 2a = 2. sin a. cos a 2 tan a tan 2a = 1 − tan2 a ch 2a = 2. ch2 a − 1 1 [cos(a + b) + cos(a − b)] 2 1 sin a. sin b = [cos(a − b) − cos(a + b)] 2 1 sin a. cos b = [sin(a + b) + sin(a − b)] 2 cos a. cos b = cos p + cos q cos p − cos q sin p + sin q sin p − sin q p+q p−q = 2. cos . cos 2 2 p+q p−q = −2. sin . sin 2 2 p+q p−q = 2. sin . cos 2 2 p−q p+q = 2. sin . cos 2 2 = 1 + 2. sh2 a = ch2 a + sh2 a sh 2a = 2. sh a. ch a 2 th a th 2a = 1 + th2 a 1 [ch(a + b) + ch(a − b)] 2 1 sh a. sh b = [ch(a + b) − ch(a − b)] 2 1 sh a. ch b = [sh(a + b) + sh(a − b)] 2 ch a. ch b = p+q p−q . ch 2 2 p+q p−q ch p − ch q = 2. sh . sh 2 2 p+q p−q sh p + sh q = 2. sh . ch 2 2 p−q p+q sh p − sh q = 2. sh . ch 2 2 ch p + ch q = 2. ch cos x = x avec t = tan sin x = 2 tan x = 1−t2 1+t2 2t 1+t2 2t 1−t2 Dérivées : la multiplication par i 1 cos2 x −1 cotan0 x = −1 − cotan2 x = sin2 x tan0 x = 1 + tan2 x = −1 1 − x2 1 Arcsin0 x = √ 1 − x2 1 Arctan0 x = 1 + x2 −1 Arccotan0 x = 1 + x2 1+t2 1−t2 2t 1−t2 2t 1+t2 n’est plus valable ch0 x = sh x sh0 x = ch x cos0 x = − sin x sin0 x = cos x Arccos0 x = √ ch x = x avec t = th sh x = 2 th x = (|x| < 1) (|x| < 1) 1 ch2 x −1 coth0 x = 1 − coth2 x = 2 sh x th0 x = 1 − th2 x = Argch0 x = √ 1 (x > 1) x2 − 1 1 Argsh0 x = √ x2 + 1 1 Argth0 x = (|x| < 1) 1 − x2 1 (|x| > 1) Argcoth0 x = 1 − x2
Documents pareils
Derivatives, Integrals, and Properties Of Inverse Trigonometric
 Derivatives, Integrals, and Properties
Of Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Hyperbolic Functions
(On this handout, a represents a constant, u and x represent variable quantities)
Derivatives, Integrals, and Properties
Of Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Hyperbolic Functions
(On this handout, a represents a constant, u and x represent variable quantities)
Animal Classe Ordre Genre chat mammifère carnivore felis
 2. Par définition, si A ∈ Mn (K), on pose det A = σ∈Sn ε(σ)
où ε : Sn −→ {±1} est la signature. Par exemple,
P
2. Par définition, si A ∈ Mn (K), on pose det A = σ∈Sn ε(σ)
où ε : Sn −→ {±1} est la signature. Par exemple,
P