USE OF DOUBLE LAYER BEAMFORMING ANTENNA TO IDENTIFY
Transcription
USE OF DOUBLE LAYER BEAMFORMING ANTENNA TO IDENTIFY
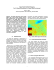
USE OF DOUBLE LAYER BEAMFORMING ANTENNA TO IDENTIFY AND LOCATE NOISE SOURCES IN CABINS Jean-Claude Pascal a and Jing-Fang Li b a Laboratoire d'Acoustique de l'Université du Maine (CNRS UMR 6613) and Ecole Nationale Supérieure d'Ingénieurs du Mans (ENSIM) ENSIM, rue Aristote, 72000 Le Mans, France b Visual VibroAcoustics, 51 rue d'Alger, 72000 Le Mans, France ABSTRACT Beamforming microphone antenna has been widely used to locate sound sources and build acoustic model. The particularities of this technique are the use of a relatively few number of microphones and simplification in the signal processing. So, this technique is fast and easy to be carried out. But its main inconvenience is the poor resolution at low frequency. In spite of this, this technique has been applied in the fields of the pass-by noise analysis, the aeroacoustic noise identification and the source localization in cabins. However, for the case of cabins, the single layer antenna does not allow one to distinguish sources located on both sides of antenna, causing difficulties to explain the results. In this paper, a double-layer microphone antenna (two layers of microphones or a layer of microphone and a layer of velocity sensors) applied in cabins is examined. This method uses the sound pressure and particle velocity of measurements together with a Statistically Optimal Array Processing (SOAP) to identify wave front of a source model. It is shown how a processing method similar to that of the sound intensity allows one to separate the contributions which come from two sides of antenna and are made by sources (leakage, radiating zones etc.) located on the walls of the cabin. Numerical simulations in a multisources environment demonstrate the interests of this technique. Keywords: Double-layer microphone antenna, Statistically Optimal Array Processing (SOAP) 1