by the numbers
Transcription
by the numbers
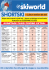
BY THE NUMBERS | TEAM SPORTS SPORTS NUTRITION FOR THE COMPETITIVE SEASON Current Recommendations from the Scientific Literature This document is designed as a quick reference of published recommendations for adults. These numbers should be used as a guide, taking into account individual factors and goals of the athlete. Every team sport is different and factors such as rules of play, frequency of games, length of season and position-specific requirements alter the nutritional plans. Daily Carbohydrate PRE-PRACTICE/GAME RECOMMENDATIONS 5-7g/kg/d 1.2-1.7g/kg/d (3) POST-PRACTICE/GAME RECOMMENDATIONS *pre-event meal Pre-Carbohydrate Pre-Fluid 1-4 h pre, 1-4 g/kg* 5-7 mL/kg 4 h pre; if urine is dark or not produced another 3-5 mL/kg 2 h pre During Carbohydrate During Fluid 30-60 g/h Based on individual sweat rate. Aim to consume an amount of fluid to minimize body weight loss (2) DURING PRACTICE/GAME RECOMMENDATIONS (1) (5,6) (1,2,3) <~2% minimize DAILY RECOMMENDATIONS Daily Protein FIBRE PROTEIN FAT Exact timing and amount should meet individual athlete preferences and time constraints. (5) Post-Carbohydrate Post-Protein Post-Fluid <8 hours between practice/competition, 1.0-1.2 g/kg 0.25 g/kg, ~20-25 g works for most athletes 1-1.5 L/kg body weight lost of fluid with sodium (2,3) (4) (1,3,6) For more in-depth information, please visit www.GSSIweb.org/en-ca and click on For Professionals. References: (1) American College of Sports Medicine, American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada. (2009). Nutrition and athletic performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 41, 709-731. (2) Burke, L., Hawley, J., Wong, S., & Jeukendrup A. (2011). Carbohydrates for training and competition. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S17-27. (3) Holway, F. & Spriet, L. (2011). Sport-specific nutrition: Practical strategies for team sports. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S115-125. (4) Phillips, S. & Van Loon, L. (2011). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S29-38. (5) Sawka, M. N., Burke, L. M., Eichner, E. R., Maughan, R. J., Montain, S. J., & Stachenfeld, N. S. (2007). American College of Sports Medicine position stand: Exercise and fluid replacement. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 39, 377–390. (6) Shirreffs, S. & Sawka M. (2011). Fluid and electrolyte needs for training, competition, and recovery. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S39-46. ® EN CHIFFRES | SPORTS D’ÉQUIPE NUTRITION SPORTIVE POUR LA SAISON DE COMPÉTITION Recommandations actuelles provenant de la documentation scientifique. Ce document est conçu à titre d’outil de référence rapide à propos des recommandations publiées pour les adultes. Ces chiffres doivent servir comme guide, tout en tenant compte des différents facteurs et objectifs individuels de chaque athlète. Chaque équipe sportive est différente et certains facteurs comme les règles de jeu, la fréquence des parties, la durée des saisons et les exigences particulières de chaque position influencent les plans nutritionnels. Glucides 5 à 7g/kg/jour 1,2-1,7g/kg/jour 3 1 Apport en glucides RECOMMANDATIONS DE CONSOMMATION AVANT UN ENTRAÎNEMENT OU UNE PARTIE Apport en liquides 1à4 1 et 4 heures avant l’activité physique* g/kg consommés entre 2 5 à 7 mL/kg consommés 4 h avant l’activité physique; si l’urine est foncée ou produite en faible quantité, consommer une quantité additionnelle de 3avant à l’activité 5 mL/kgphysique 2 heures 5,6 Glucides RECOMMANDATION DURANT L’ENTRAÎNEMENT OU LA PARTIE Réduire au minimum la consommation de RECOMMANDATIONS QUOTIDIENNES Protéines * lors du repas qui précède l’activité physique FIBRES PROTÉINES LIPIDES Le moment exact de la consommation et les quantités à consommer doivent être ajustés en fonction des préférences de chaque athlète et de ses contraintes de temps. Liquides 30-60 g/heures 1,2,3 En fonction du taux de sudation de chaque personne. Cherchez à consommer une quantité de liquide qui vous permet de compenser la perte de masse corporelle <~2% 5 Glucides RECOMMANDATIONS DE CONSOMMATION APRÈS L’ENTRAÎNEMENT OU LA PARTIE Protéines Liquide 1,0 à 1,2 g/kg 0,25 g/kg: un apport approximatif de au moins 8 heures avant la séance d’entraînement ou 20 à 25 g est adéquat la compétition suivante pour la plupart des athlètes 2,3 1 à 1,5 De L/kg en masse corporelle perdue avec du sodium1,3,6 4 Pour obtenir plus de détails, visitez le site www.GSSIweb.org/fr-ca et cliquez sur l’option « Pour les professionnels ». Références : (1) American College of Sports Medicine, American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada. (2009). Nutrition and athletic performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 41, 709-731. (2) Burke, L., Hawley, J., Wong, S., & Jeukendrup A. (2011). Carbohydrates for training and competition. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S17-27. (3) Holway, F. & Spriet, L. (2011). Sport-specific nutrition: Practical strategies for team sports. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S115-125. (4) Phillips, S. & Van Loon, L. (2011). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S29-38. (5) Sawka, M. N., Burke, L. M., Eichner, E. R., Maughan, R. J., Montain, S. J., & Stachenfeld, N. S. (2007). American College of Sports Medicine position stand: Exercise and fluid replacement. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 39, 377–390. (6) Shirreffs, S. & Sawka M. (2011). Fluid and electrolyte needs for training, competition, and recovery. Journal of Sports Sciences, 29 Suppl 1, S39-46. ®