bcl-2
Transcription
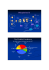
bcl-2
Case # 10 (P585853) • 25 year-old man • Recurrence of a swelling left node in the groin • Patient followed for a « lymphoma », diagnosed 3 months earlier ---à needle biopsy (relapse?) To note FISH study for c-myc: rearrangement of c-myc What to do ? • • • • • • • • • • Review the initial slides Ask for another specimen CD20, CD5 ou CD20, CD3 Tdt CD10, CD23, Bcl-2 Bcl-1 Bcl-6 MIB1/Ki67 Other : ??? Make you choice, ….!!! CD20 CD5 Review of the initial lymph node biosy… CD20 IgD CD5 Bcl2 To note FISH study for c-myc: rearrangement of c-myc What else ? • FISH studies (parrafin sections) (split probes): - c-MYC rearrangement - absence of Bcl2 rearrangement - absence of Bcl6 rearrangement BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA • MORPHOLOGY : proliferation lymphoid cells - diffuse - cohesive monomorphic - regular medium/large - starry-sky pattern • B-cell PHENOTYPE : - CD10 + (s), CD5- IgM+ - bcl-2 -, MIB1 + (all cells) • CYTOGENETICS : - t(8; 14) (q24; q32) - or variants t(2;8), t(8;22) - involve c-myc R • CLINICAL DATA: - children (++), adults - Endemic : Africa, EBV+ - Sporadic: intestinal DLBCL • polymorphism: cbs, Ibs • variable proliferative rate (MIB1/Ki67 (30-95%) • CD10- (+) • bcl-2 protein + (-) • cytogenetics: 3q27(30%), t(14;18) (20%), c-myc R (10-20%) • EBV association (10%) Burkitt • cohesive, monomorphic lymphoid cells; no Ibs • high proliferative rate (mitosis, MIB1/Ki67=100% ) • CD10+ (s) • bcl-2 protein • t(8; 14) or variant ------> c-myc R (100%) (Iry event) • EBV association (25%, sporadic to 100% (endemic) • frequent CNS, BM involvement Case # 10 Proposed diagnosis Burkitt lymphoma (poor morphology) • Diagnostic feasible on a core needle biopsy based on a combination of phenotypic & cytogenetic criteria, in the context of a patient followed for a typical BL • Crush artefacts and poor cytology are frequent in «aggressive» lymphomas • BL is characterized by a « simple » karyotype comprising translocation fusing c-MYC with Ig genes Conduite à tenir devant des artéfacts d ’écrasements • Liés à pince ET à fragilité des cell. Tumorales (CPC, LNH,..) • prélévements en zone peu accessibles (Ex: médiastin) • Valeur ++ : - contexte clinique - IHC (cytok, CD20, CD3, MIB1,....) • L ’IHC pourra affirmer la nature de la lésion tumorale, préciser certains détails cytologiques cell. tumorales,… Ponction-biopsie à l’aiguille: CAT ? 1. Proscrire pour les gg périphériques; valeur masses profondes 2. Grandes cellules diffus: à priori pas de pb; valeur cyto et MIB1 3. Petites cellules: pb car pas d’architecture; nénmoins l’IHC peut résoudre d’assez nombreux problèmes: - sous-classification pfs pas possible (confrontation clinique) - exiguité du pt à indiquer, pouvant gêner l’appréciation d’une éventuelle transormation 4. Infiltrats T « à petites cell »: pas de valeur; se méfier Hodgkin